Lab for Innovative Infrastructure Systems > Research Activities > Bachelor/Master's/Doctoral Theses > Bachelor/Master's/Doctoral Theses
Bachelor/Master’s/Doctoral Theses
Please click on the title for the abstract of the thesis. Moreover, please click on the figure to enlarge it.
Year 2021
Master’s Theses
With the recent development of information technology, the collection and provision of traffic information is expected to play a more important role in the future. On the other hand, it has been found that the provision of traffic information to vehicles is not always socially effective in general. Rather than the perfect information, which always provides correct traffic information, there are cases in which no information or partially correct information mixed with noise. Information design, a field of game theory, deals with such information provision problems. Information design considers the influence of information on the behavior of other economic agents in an environment with uncertain state, and analyzes the information structure (optimal signal) that produces the optimal result for the sender of the information. In this study, a traffic information model focusing on demand uncertainty was developed using an information design framework. Moreover, optimal signals for the sender and traffic manager were derived and analyzed. The mechanism design approach and the belief design approach, both of which are information design methods, were used to derive and analyze the optimal signal for the sender, who is the traffic manager. For each approach, the sender is the driver, and traffic models were created in two settings: one in which the sender wants to minimize the total cost to the driver, and the other in which the sender wants to allocate the traffic to the optimal traffic ratio. The mechanism design approach showed that in both settings, optimal signals may improve the results over perfect or no information. In the belief design approach, the optimal signal was always found to be the provision of complete information in the total cost minimization setting. On the other hand, in the optimal traffic allocation setting, it sometimes resulted in an improvement over perfect or no information. In particular, we analyze in detail the parameter settings in which the optimal signal is equivalent to no information or perfect information. Finally, we compared the characteristics of both the mechanism design approach and the belief design approach in setting up the traffic model in this study, and found that the mechanism design approach with individual signals was more effective in the traffic model in this study..
In recent years, the worldwide COVID-19 pandemic has brought some major changes in people’s behavior. The rail demand structure has changed due to more flexible work styles, such as telecommuting and staggered commuting, among rail commuters in the Tokyo metropolitan area. Under these circumstances, railroad operators in the Tokyo metropolitan area and the government are considering the introduction of time-of-day fares, a fare system that aims to equalize congestion by charging an additional fare during peak hours. In considering time-of-day fares, it is necessary to predict how the new coronavirus will affect the departure time selection behavior of urban rail commuters before setting fares. In this study, a departure time choice model and a passenger demand assignment model were constructed for a situation in which commuters with fixed arrival times and flexible commuters simultaneously choose a train, using the framework of a multi-class allocation model. By using these models, time-based faring simulations were conducted for each of four post-corona scenarios (1. increase in telecommuting, 2. increase in flextime, 3. increase in aversion to congestion, and 4. promotion of migration to the suburbs). We also evaluated congestion rates and the total fare revenue that the rail operators could obtain from time-of-day fares. Prior to the simulation, we analyzed the number of people staying in the area using location information from cell phones in order to understand the actual behavior of people during a new coronavirus epidemic. As a result, we confirmed changes in the population staying within the mesh of major radial routes in the Tokyo metropolitan area during a novel coronavirus epidemic. In the time-of-day faring simulation, many-to-one unidirectional routes from multiple suburban stations to a single central city station were analyzed. The results of the scenario-by-scenario analysis suggest that as measures that directly change the demand structure of commuters (telecommuting, flextime, suburban migration) are implemented, congestion rates level off, and the total revenue from rail operators’ charges decrease accordingly. The results also suggest that as the aversion to congestion increases, congestion rates level off, literally to avoid congestion, and the total revenues of railroad operators decrease accordingly. In addition to the scenario-by-scenario analysis, an analysis of the Seibu Shinjuku Line was conducted to consider the application of the model to a real railroad line. The results showed that the results were equivalent to those of the scenario-by-scenario analysis, indicating that the model can be applied to the actual line.
In recent years, overtourism due to an increase in the number of tourists has become a global problem. In some areas, the introduction of congestion pricing is being considered as a countermeasure, but many of the existing examples of introduction target urban centers where commuter traffic is prominent. It is difficult to predict the effect of policy introduction. In this study, we constructed an activity-type traffic behavior model for sightseeing excursions by extending the framework of the mixed integer programming problem. Then, we calculated the dynamic user equilibrium allocation of the tourist movement and activity schedule considering the increase in travel time due to congestion, and predicted the change in the amount of sightseeing excursions. We predicted changes in traffic demand in tourist areas when traffic demand management measures were introduced, and evaluated the effects of the measures. A virtual network that assumes the “(tentative name) Kamakura Road Pricing” that currently being considered in Kamakura City. Then, based on the visitor survey conducted by Kamakura City, we set up multiple tourist groups with different characteristics and predicted the tour behavior of tourists. In addition, from the viewpoint of the impact on the road network and tourists, we evaluated four types of policies with different charges. As a result of the analysis, it was shown that the congestion situation of the road network was improved as the charging amount was increased. In general, the impact on the decrease in vehicle share is remarkable, and it was confirmed that the introduction of congestion charging and the setting of the amount can contribute to the control of the inflow of vehicle traffic. Furthermore, it was suggested that a synergistic effect with other traffic demand management measures could be expected because of the shift to park-and-ride. Additionally, since the total travel cost of tourists also increases as the charge amount increases, it was suggested that a high charge setting reduces the utility of tourists and reduces the attractiveness of tourist destinations. From the above, it was shown that the congestion of the network is resolved as the fee increases, but the utility of tourists decreases.
Currently, more than half of the daily trips of people in the Tokyo metropolitan area in Japan are simple round-trips between home and workplace. MaaS, a new mobility service, is expected to promote mobility by integrating information and fare systems among transportation modes to increase convenience. In this study, an activity-based transportation behavior model was constructed to evaluate the change in people’s activities due to the introduction of MaaS, taking into account the impact of subscription services (a service that allows unlimited use of transportation services on a certain section of road by paying a fixed fee). In this study,the focused on commuter passes holders in order to evaluate the introduction of MaaS even from current data before the introduction of MaaS. Specifically, the commuter pass is viewed from the perspective of “using a commuter pass that allows free access to a certain area by paying a subscription fee,” and the expanded version of this service is considered as MaaS. The model structure is based on the assumption that after selecting an activity pattern, people first decide whether to go within or outside the subscription range, and then decide on a specific destination or route, thus creating a two-stage destination selection model. The parameter estimation results showed that women and those under 20 years old were more likely to choose within the commuter pass range, while those with more than 150 minutes of available remaining time were more likely to choose outside the commuter pass range. In addition, women and those who had more than 90 minutes of free time remaining were more likely to take side trips. Using the model, simulations were conducted for the Yamanote and Tobu-Tojo lines, when MaaS was introduced to each line. The activity change was found to be an increase in detour trips for all age groups after the introduction of MaaS. For the subscription fee, the maximum willingness to pay was quantitatively computed for each of the individual attributes and home and workplaces. The values were found to be higher for females and those under 20 years old, and lower for those whose homes were farther away from the MaaS introduction area.
Bachelor Theses
For autonomous decentralized traffic management that improves traffic flow by providing appropriate traffic information, Iwase et al. proposed the concept of self-fulfilling signals, an information provision method that suppresses the phenomenon of traffic flow oscillation (hunting). Ukai and Fukuda verified the effectiveness of self-fulfilling signals in suppressing hunting through a group indoor experiment. However, the experiments were too small to properly analyze the hunting suppression effect. In this study, we conducted an interactive online route choice experiment in which a larger number of agents participated, and analyzed the effect of self-fulfilling signals on hunting inhibition. The experimental results showed that the hunting was suppressed when the scatter of traffic information based on self-fulfilling signals was large. Furthermore, we conducted a statistical analysis of information compliance behavior at the individual level using the Mixed Logit Model, and clarified the determinants of compliance behavior.
This study quantifies and ex-post evaluates the impact of the Place-Based Policies implemented in Japan in recent years on the population distribution and regional economies of the entire country. We constructed a prefecture-based multiregional model based on quantitative spatial economics (QSE) that takes into account interregional population movements and agglomeration economies, and analyzed the impact of four types of interregional allocation policies. The results of a counterfactual simulation of the case in which the policies were not implemented suggest that while the policies reduced the gap in the number of workers between prefectures. It also reduced the total national real income and that the effects of the interregional allocation policies were not limited to short-term effects but persisted over the long term. Furthermore, the results suggest that a decline in Japan’s total population will accelerate the outflow of population from regional areas.
Year 2020
Doctoral Thesis
The purpose of this study is to model the spatio-temporal pattern of freight trucks and to analyze empirically its applicability of policy analysis. The following three aspects of urban freight traffic are considered: (1) modeling and policy analysis of urban freight traffic using large-scale statistical freight survey, (2) analysis and modeling of freight trucks’ route choice behavior considering vehicle types and trip length, (3) analysis and modeling of freight trucks’ tour choice behavior considering time axis. We analyzed and modeled the freight traffic from the three viewpoints and discussed the policy of urban freight traffic. The main results of this study are as follows. The first result is a systematic review of modeling methodologies for logistics activities. Many modeling methods have been proposed that consider the behavior and decision-making processes of individual agents in logistics activities. We systematically reviewed these studies and summarized the focus and approach of each modeling. The second result is the modeling of freight vehicle traffic based on non-route-enumerated behavioral models. In this study, we modeled urban freight trucks’ behavior for the quantitative evaluation of freight traffic policies. The third result is an empirical analysis and policy simulation of urban freight traffic. In this study, based on the constructed model, an empirical analysis of urban freight traffic and policy simulations was carried out. In summary, we modeled the spatio-temporal patterns of freight trucks based on vehicle trajectory data and non-route-enumerated models, and empirically analyzed their potential for use in policy analysis. The analysis suggests that strong policy interventions may cause external diseconomies (deterioration of living conditions, concentration of freight traffic at certain times of the day, etc.) and that systematic regulation and guidance of freight traffic may be necessary.
Master’s Theses
Tourism development as one of the focusing strategies of Japanese government has successfully boosted the economy in recent years. On the other hand, as the tourism prospers, however, it brings much worries in over-tourism problem. The Yaeyama Region as a case of this concern. In order to grasp the patterns of tourists and their characteristics in Yaeyama Region, this paper will discuss about the patterns in mainly two perspectives by using the Wi-Fi data and Bluetooth data. In the first perspective, this paper will show how do visitors using different transportation means tour around at the indexes of time duration period and trip chain pattern. Besides, a brief discussion of differences between Wi-Fi sensing and Bluetooth sensing in the capture result. In the second perspective, this paper will analyze and forecast the variations of visitors’ numbers in each detecting spot by applying a time series analysis method. Based on the conclusions, this paper will contribute in picturing tourists’ patterns and correlation between time and choices of visit places.
While the tourism demand has increased in recent years, the overtourism problem has occurred in tourist areas. Kamakura, one of Japan’s leading tourist destinations, also suffers from traffic congestion due to visitor traffic on holidays. However, in tourist areas where the capacity of existing railways and bus routes is insufficient compared to metropolitan areas where commuter traffic is the main traffic, the shift from automobile traffic may bring further congestion to other modes of transportation. In addition, it is necessary to model tourism behaviors that accompany excursions within a region in more detail on a day-to-day tour basis in order to appropriately grasp changes in traffic demand accompanying the introduction of policies. In this study, mHAPP, an activity-based model considering the congestion effects, is constructed by extending the framework of the mixed integer programming problem under the situation where multiple transportation modes are available, in order to appropriately grasp the changes in tourism transportation demand associated with the introduction of the congestion charging policy. Using the model, we predicted changes in tourist excursion patterns under the introduction of a congestion charging policy and under the condition that capacity within the public transportation system is taken into account. The model was also used to evaluate the impact of the introduction of the policy on tourists in terms of tourist satisfaction. In the analysis, a simplified traffic network of Kamakura was created assuming the hydrangea season in June. Using cell phone base station data and other data, we identified typical tourist excursion patterns and their share in the transportation network, and targeted the tourist groups with these excursion patterns for analysis.
In recent years, the development of Urban Air Mobility (UAM) has been promoted worldwide. In particular, both the public and private sectors have begun to consider the concept of UAM passenger services in urban areas and their outskirts using small electric passenger planes. In this study, a mathematical planning model for UAM passenger service operation that takes into account users’ transportation choices is developed, and factors that may increase the service introduction effect on users while ensuring a profitable service operation are examined from both the service provider’s and user’s sides. Dominant factors that are important for the future introduction of UAM passenger services are clarified. The study also provides a basic insight into the potential use of UAM for passenger transport in Japan, especially to the outer fringes of the country, starting from Tokyo. We considered that the potential users of UAM are people with high travel time value who use railroads in urban areas in Japan, where public transportation networks are well developed. We constructed an integer linear optimization problem in which service operations, including aircraft recharging and operational income and expenditure at nodes, and users’ transportation choices interact with each other.
Chronic train delays have become a problem for railroads in major metropolitan areas. The delay phenomenon is caused by a complex combination of various factors, such as train running/dwelling times and weather conditions. Previous studies have attempted to investigate this phenomenon using mathematical models and simulation models. However, there are few studies that reflect real phenomena and clarify the detailed mechanism of delay phenomena. Moreover, there are few studies that consider weather conditions, one of the delay factors. Therefore, this study aims to construct a probabilistic graphical model, Bayesian Network (BN), that shows the spatio-temporal relationship between stations and trains in urban railroads. The objective is to quantitatively analyze the occurrence structure of the phenomenon and the influence of weather conditions, using second-by-second data of the Tokyo Metro Tozai Line over a long period of time and data from the Japan Meteorological Agency. Before building the model, the relationship between rainfall and the number of seconds of train delay was analyzed. The results showed that the delay time of arrival and departure at each station tends to be larger on rainy days, and that the delay time is the largest during the 8:00 a.m. peak period. Based on the above, a BN model was constructed using the actual operation data. In the model, a node was created for each train departure and arrival at each station, and the delay phenomenon was analyzed by explicitly treating each station and train. A precipitation node was created for each station to reproduce precipitation conditions at each station and at each time of day in detail. Using the model created in this way, we conducted “structural learning” to learn data and clarify relationships among trains, “probabilistic inference” to reproduce the number of seconds of delay by inputting time precipitation as observed values, and “sensitivity analysis” to determine the influence of explanatory variables based on the amount of mutual information.
Bachelor Thesis
DSRC, a new information and communication technology in the road traffic field, can acquire a wider variety of information than conventional technologies. However, the only data that can be collected in real-time is traffic volume information, while the information on speed and density from existing fixed detectors, is not available. In this study, we developed a method to detect abnormal events such as flooding in real time using only the traffic volume obtained from DSRC. In particular, the method is unique in that it uses a Bayesian deep learning model framework for both the immediate and precise detection of abnormal events. The usefulness of the proposed method was verified through an analysis of the road network in the Kanto area.
Year 2019
Doctoral Thesis
Traffic congestion is a serious problem in cities. In past decades, the transporta- tion infrastructure has expanded to meet an increased travel demand. As a result, multiple transportation modes are used in most cities. However, building the trans- portation infrastructure is an expensive strategy and increases the travel demand. Moreover, public transportation faces serious congestion. Thus, an efficient transportation system where multiple modes are available under travel demand man- agement is important to the mitigation of congestion. To understand the mechanism of congestion, models at the microscopic level (i.e., link level) have been used in the literature. However, Daganzo [1998] reported that microscopic modeling might be limited for cities with a highly complicated traffic demand in space and time. The parsimonious model with a few variables can be used to tackle this problem. The macroscopic fundamental diagram (MFD) is one such model. It relates the spatial mean flow to the spatial mean density. The present thesis focuses on the problems (I) that the well-defined MFD cannot be observed if the network is heterogeneous and (II) that although the three-dimensional MFD (3D-MFD) captures the congestion dynamics of a bimodal (e.g., car and bus) transportation system, control strategies that mitigate congestion on the basis of the 3D-MFD have rarely been investigated in the literature. The objectives are thus to conduct a cross comparison of network partitioning methods to find an optimal area having a well-defined MFD using real traffic data and to propose an analytical and simulation-based framework for the optimization of bimodal transportation systems. First, we conduct a cross comparison of spatial partitioning methods to identify the optimal area. The normalized-cut-based approach proposed by Ji and Geroli- minis [2012] and community-detection-based approach proposed by Ge et al. [2016] are compared. We take the Tokyo central business district as a case study using traffic data recorded by an enormous number of detectors. We then investigate the advantages and disadvantages of the two approaches in terms of applicability. Second, we develop a bimodal morning commute for cities, focusing on departure time and transportation mode choices in bimodal transportation systems, to inves- tigate analytically the properties of bimodal systems, such as the area-wide effect of a dedicated bus lane. Our model incorporates the 3D-MFD congestion dynamics and crowding discomfort in buses. Properties of the no-toll equilibrium are inves- tigated and the patterns of the departure rate and congestion and the relationship between the equilibrium cost and the ratio of the dedicated bus lanes are obtained for a numerical example. Third, we propose a simulation-based joint optimization of congestion pricing and dedicated bus lanes for congestion mitigation in bimodal transportation systems. We develop (I) a joint optimization framework of the congestion pricing and dedicated bus lanes, (II) an area-based congestion pricing scheme relying on the 3D-MFD, and (III) a framework that combines a microscopic traffic simulator with the travel behavior of the individual (i.e., departure time and transportation mode choices). We then consider the Tokyo central business district in a case study and show the efficiency of 3D-MFD-based pricing compared with that of single-mode-MFD-based pricing.
Master’s Theses
The transit-oriented development (TOD) is expected to bring externalities, one of which is indirectly affecting the residential land values within the area. In Tokyo and its suburbs where people are heavily dependent on train networks, some station-area neighborhoods and railway lines operated by different railway companies may have intrinsic values, caused by either the quality and service of each neighborhood and line or other, unobservable traits. In this paper, the effects of TOD characteristics and different railway lines on residential land values are analyzed by utilizing the multiple membership multilevel model. The empirical result emphasizes three things. First, several TOD factors significantly affect residential land value. Second, differences across railway lines are responsible for creating a large share of land value variations. Third, the effects are the largest for the lines serving areas south to west of Tokyo in comparison with other selected railway lines.
In the evaluation of transportation-related infrastructure projects such as high-speed rail, measurement and evaluation have focused on direct benefits such as time-saving benefits. In recent years, the concept of economic effects and benefits in a broader sense has been proposed in addition to time-saving benefits. While empirical studies on the evaluation of these benefits have been accumulating, they are insufficient. In this study, we focus on the changes in the working population of each industry, which is one of the economic benefits in a broad sense, and empirically clarify how these changes will be affected by the construction of high-speed rail. Using data on the working population by municipality, we applied a difference-in-differences analysis and found that the working population of the wholesale and retail industry increased from 2.4% to 8.2% in municipalities where high-speed rail stations were constructed, suggesting the possibility of regional specialization in these industries.
With the development of sensing technology, it has become possible to collect a variety of traffic information in real time, and research on short-term prediction of traffic conditions using this information is progressing. However, there are few examples of traffic volume forecasting for sightseeing spots, and its application to the evaluation of overtourism is insufficient. In this study, we developed a multivariate LSTM-based learning model that can comprehensively take into account various characteristics such as the day of the week, season, weather, and event information in order to accurately forecast traffic volume in tourist areas. Specifically, the model outputs a 60-minute forecast of traffic volume in the central area of Kamakura City by learning multiple inputs such as traffic volume data, precipitation, and social event information. The results showed that the model had relatively high performance in forecasting traffic volume in mid-June, a peak season, with an average absolute error rate of 7.03%.
Thanks to the development of information and communication technologies (ICT) and the diffusion of teleworking, it may recently be possible for workers to select workplaces. If a working space such as a large-scale satellite office is set up in the suburbs, there might be a possibility of providing new work styles by which train congestion can be avoided and thereby the quality of life may be improved. The study analyzed the changes in the commuter’s daily activity patterns that could occur due to such urban policy in the Tokyo metropolitan area. By conducting a large-scale questionnaire survey to unveil the degree of usage intention of satellite center-based teleworking in terms of commuting conditions, the study estimated an activity-based travel behavior model with considering choice behavior of working place.
In the spread of electric vehicles (EVs), charging characteristics such as short range and lack of charging facilities are issues that need to be resolved. Moreover, a comprehensive evaluation that considers the strategic behavior of users (consumers) should be conducted in the planning of charging facility locations. In this study, we developed a mathematical model to evaluate the interdependence between EV route choice behavior (short-term decision making) and consumer vehicle type selection behavior (long-term decision making) in a road network where multiple types of charging facilities are deployed. We confirmed the basic behavior of the model through some simple numerical calculations, it is possible to conduct a more precise evaluation of the shortage of charging facilities, taking into account network externalities and long-term EV demand fluctuations.
Bachelor Theses
It is known that the phenomenon of traffic oscillation called hunting occurs when drivers are provided with incomplete traffic information, and Iwase et al. proposed the concept of self-fulfilling signals, an information provision method that avoids this phenomenon. However, this study is limited to a simple analytical model, and the effect when a human actually receives a signal and chooses a route is unknown. In this study, we conducted small-scale experiments to verify the realistic validity of hunting suppression by self-fulfilling signals. We constructed a simple experiment environment in a virtual network and analyzed data obtained from a group route choice selection game. Next, we conducted a numerical simulation analysis simulating a typical route choice norm in the experimental data, and clarified the relationship between choice behavior and the signal effect.
In this study, we focus on the subscription-type MaaS, which allows users to use multiple mobility services for a fixed fee, and construct a method to quantitatively evaluate the relationship between the set spatial range of subscription-type MaaS and the maximum allowable (fixed) fee for each service from the viewpoint of transportation behavior analysis. Specifically, we developed a multimodal transportation choice model using a recursive logit (RL) model, and proposed an idea to apply the RL model to trips using multiple transportation modes within a set area of a subscription-type MaaS, focusing on the route de-enumeration property of the RL model. To verify the realistic validity of the proposed approach, we estimated the parameters of the RL model using the Tokyo metropolitan area PT survey, and conducted a simulation of the introduction of MaaS in a specific area. The simulation results show that the proposed evaluation method can appropriately change the calculated allowable flat rate depending on the range of application of MaaS and the characteristics of the target OD pairs.
Year 2018
Master’s Theses
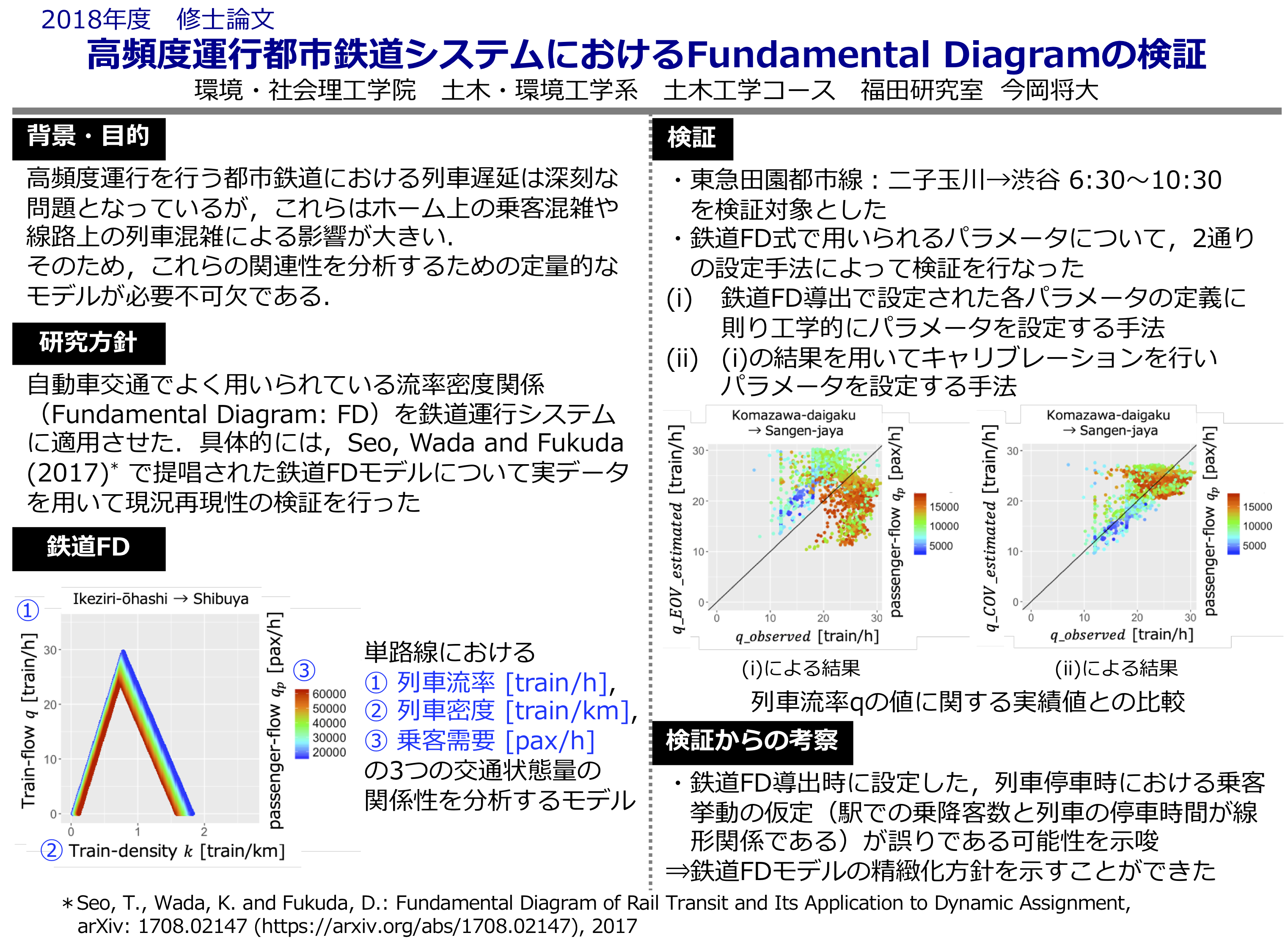
While many urban railroads in the Tokyo metropolitan area operate high frequency services to meet high demand as much as possible, once delays occur, they tend to be chronic due to various types of congestion. This type of delay is a pressing issue in train operations because it occurs on a daily basis. To solve this problem, it is necessary to develop a quantitative analysis method that enables appropriate understanding of train delay phenomena and evaluation of delay countermeasures, taking into account the train-passenger relationship. In this study, the validity of a theoretical model for the flow-density relationship (Fundamental Diagram) considering the train-passenger behavior was verified using actual train operation data, and it was confirmed that the calibration results showing a certain degree of reproducibility to the current situation.
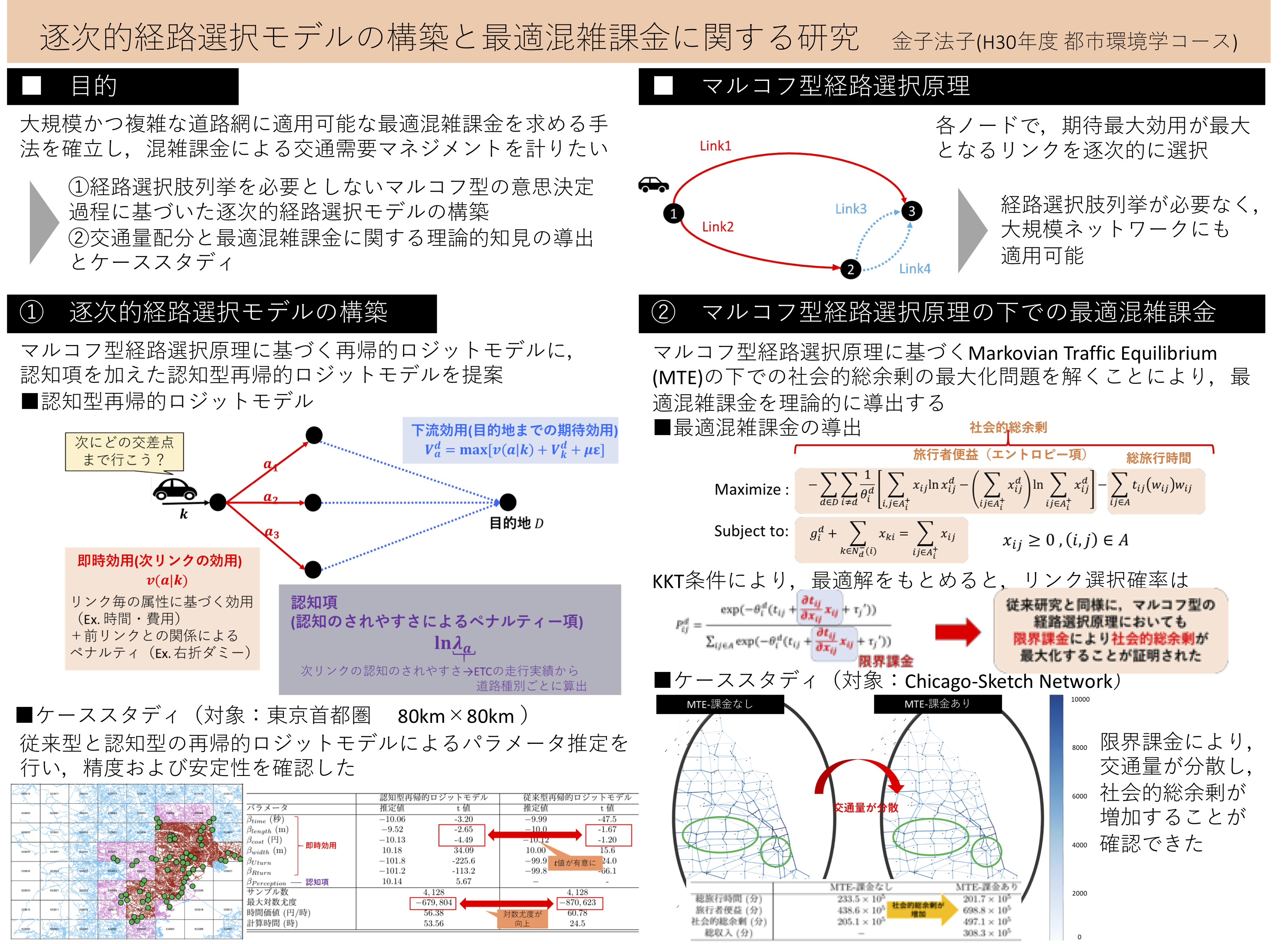
In this study, we constructed a cognitive RL model that takes into account the effect of cognition and estimated parameters of a large-scale route choice model for the Tokyo metropolitan area. We confirmed that the model improves the estimation stability compared to a conventional model. We also theoretically showed that the marginal charging principle holds for optimal congestion charging and optimal system allocation under the Markovian route choice principle as well as the path-based case by formulating an optimization problem with total social surplus maximization as the objective function. We then conducted an empirical analysis on a real network and confirmed that marginal charging improves the network.
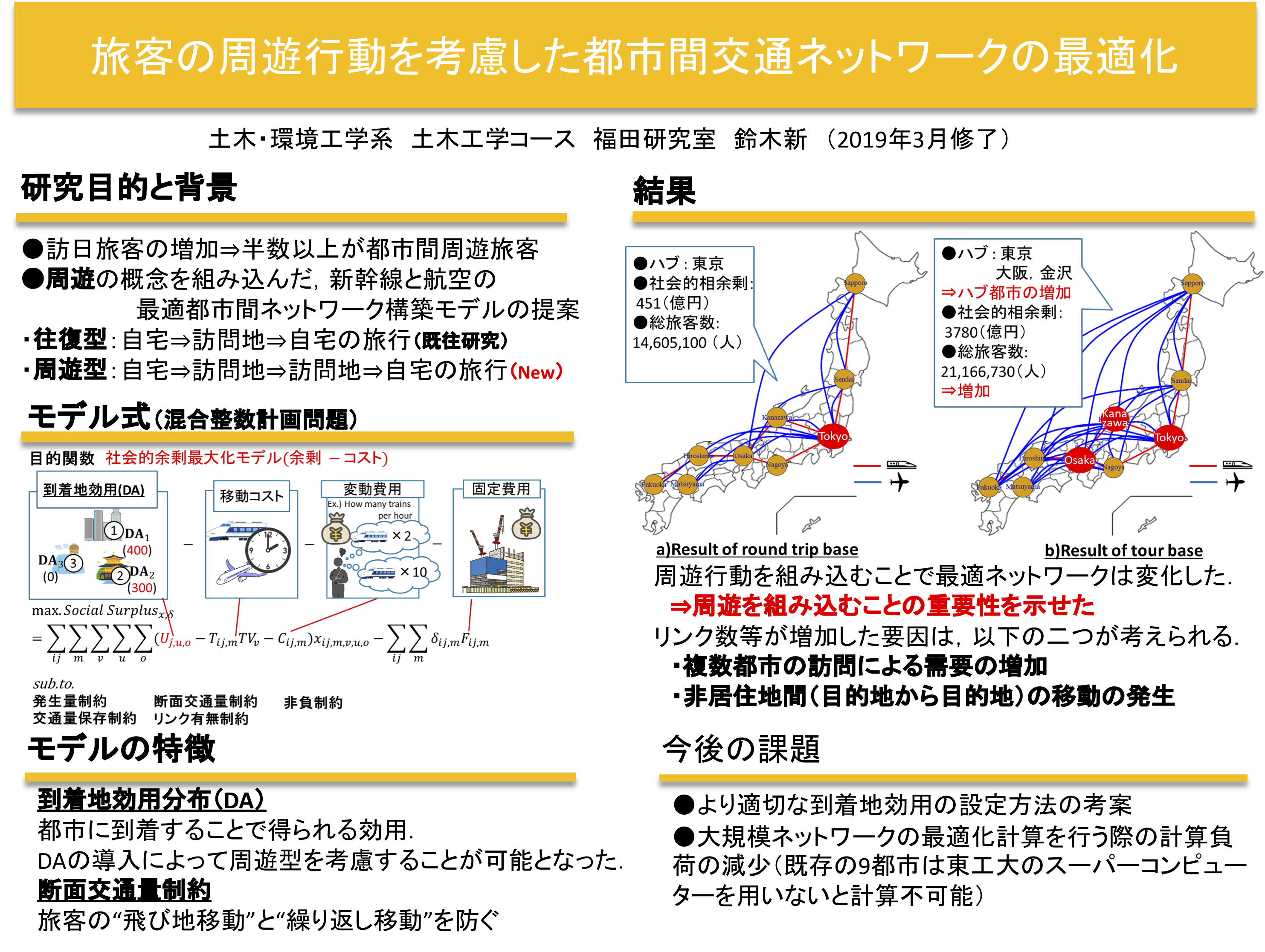
It is important to study the social optimal network for the intercity transportation network such as bullet trains and airplanes. In recent years, the number of intercity travelers who travel not only between their residence and one city but also between multiple cities has been increasing. However, conventional network planning models do not take this into account. In this study, an optimal network planning model for the Shinkansen and airline network that takes into account passenger excursion behavior is developed in the framework of mixed integer linear programming. Sensitivity analysis of the optimal network shape under different travel modes (round-trip and excursion) suggests that regions that are not connected in the round-trip model may be connected in the excursion model. Finally, the proposed method was applied to the national main line transportation network to confirm its usefulness.
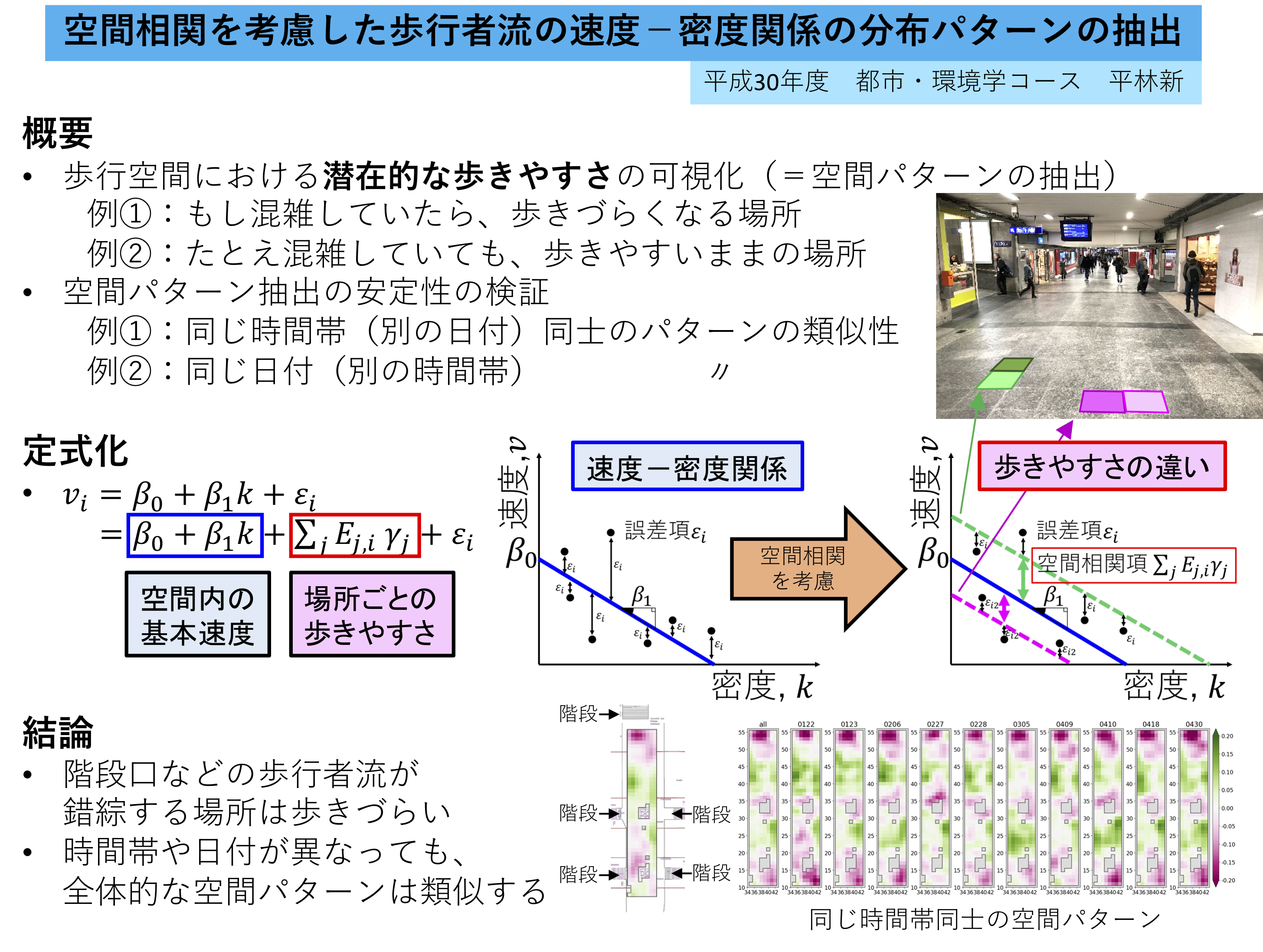
With the construction of a detailed evaluation method for walking space, we extracted spatial patterns that enabled us to understand local spatiality by using detailed pedestrian movement trajectory data. The obtained spatial patterns were reasonable, suggesting speed reduction in the vicinity of obstacles in real space. The results of the application to a large amount of data were compared within a day and between days, and the global stability of the patterns was shown. Finally, the statistical significance and consistency with intuitive congestion/non-congestion of statistical similarities among multiple patterns were confirmed.
Despite ride-sharing can increase the accessibility of areas with limited transport offer, drivers sharing their rides may not be willing to detour for collecting passengers in areas with low demand, such as rural areas. We analyse the introduction of an economic incentive in an intercity ride-sharing platform to encourage drivers to stop in small towns along their route. By conducting simulation analysis in a synthetic network, our results show that social welfare is maximised when the economic incentive is about 3.3 times the value of travel time when the demand and supply are balanced. However, individual welfare gains were found small. When passengers have a high value of travel time, the incentive had a negative impact on social welfare. Incentive had a negative impact on the income of the platform provider.
Bachelor Thesis
Analyzing the intention to use new transportation services using fully automated driving is useful in examining the ideal direction of mobility in the near future. However, it is generally believed that Japanese people are psychologically resistant to the use and share of new technologies, and it is necessary to conduct an analysis that explicitly considers such influences. In this study, we analyzed the determinants of intention to use a ride-sharing system with fully automated vehicles by conducting a questionnaire survey asking about psychological images of automated ride-sharing and Stated Preference (SP) for possible future hypothetical usage conditions. The results suggest that high preference for new products and general risk aversion tend to influence the intention to use the service, and that people prefer a situation in which others of the same sex are riding in the car for a short period of time when they use the service.
Year 2017
Master’s Theses
The occurrence of life-coarse events (e.g., moving, childbirth, etc.) of a household has been considered to have a significant impact on its car-owning behavior. However, many previous studies have used cross-sectional data only for a single point in time, making it difficult to strictly grasp the causal relationship. This study aims to clarify the effects of life-coarse events on changes in household car-owning behavior using long-term, large-scale panel data on car ownership and car usage. After conducting a basic aggregate analysis, we estimate models for changes in ownership status, changes in vehicle type, and purchases of new vehicle types, as well as a model that integrates these models. For example, it was confirmed that a large decrease in the number of people living together in a household and in the number of license holders causes the the household to give up a car.
In a wide area such as Hokkaido, there is a limitation of the implementation of questionnaire surveys and probe person surveys in terms of cost and representativeness of data in capturing sightseeing excursion behavior over a long period of time. In this research, we collect tour data of tourists in Hokkaido using a Wi-Fi packet sensor, which can efficiently collect traffic behavior data over a long period of time and over a wide area. We built a tour behavior model and confirmed the reproducibility of the current state of tourist excursion behavior using the model. Moreover, a simulation was performed to analyze the impact of demand distribution measures in areas where tourists tend to concentrate. As a result, we demonstrated the usefulness of the Wi-Fi packet sensor to a certain extent for sightseeing traffic surveys and excursion behavior analysis.
While the modern metropolitan area has developed a logistics network with the construction of three ring roads and other transportation infrastructure, there are also some problems to be considered, for instance, the mixing of freight vehicles and passenger vehicles. For this reason, it is highly important to construct a behavior model for freight vehicles. Until now, empirical analysis of freight vehicles has been conducted on a trip-by-trip basis. On the other hand, it is natural to assume that the original movement patterns of freight vehicles are generated on a per-tour basis. Therefore, this study constructs a tour pattern model that travels to multiple destinations using the results of the Fifth Tokyo Metropolitan Area Freights Flow Survey. The estimated model is then used in a policy simulation to demonstrate the effectiveness of a tour-based model as an alternative to the conventional trip-based model.
The hollowing out of city centers in provincial cities is an urgent issue. As a countermeasure, location optimization plans have begun to be planned and implemented with the aim of improving urban efficiency. The purpose of this study is to empirically and comprehensively clarify the factors that cause commercial facilities to locate or withdraw from urban areas in Gunma Prefecture. To this end, to analyze the impact of the implementation of detailed regional urban planning such as the Location Optimization Plan, we constructed a 1 km mesh-based prediction model for the number of locations and withdrawals, taking into account public transportation factors and spatial effects. The simulation results of the location optimization plan showed that the number of stores increased in the central city area, but decreased in the urban area as a whole. However, the results suggest that the downward trend can be stopped.
Bachelor Theses
With the increase in the number of inbound tourists and the diversification of private activities, the need to properly understand tourism flows has become more important than ever before, but it is still a challenge to efficiently and appropriately capture the characteristics of tourism. In this study, we attempted to extract the characteristics of sightseeing patterns around the main island of Okinawa by using Wi-Fi packet sensing, a new method of surveying traffic behavior. Sensing devices were installed at dozens of locations on the island for approximately one month, and a large amount of unique ID log data was collected. From this data, we extracted only those data that had a high probability of being tourists who entered and exited from the airport or cruise ship terminal. Then, a probabilistic block model method was used to identify typical sightseeing tour patterns, which can be clustered according to a small number of “user characteristics” × “visited spot characteristics. We also tested a prototype of a sightseeing spot recommendation system based on the non-negative matrix factorization method.
Expressway toll setting plays an important role in traffic demand management, in addition to the profitability of road construction and maintenance costs. In this study, we conducted a causal effect analysis on the impact of toll policies on traffic demand, targeting the new toll policies (specific policies on new expressway tolls in the Tokyo metropolitan area) that came into effect in April 2016. When a panel analysis with a higher evidence level was applied to the ETC total traffic volume for each IC pair, the existence of a causal effect according to the degree of toll change before and after the policy was statistically suggested. Furthermore, when we estimated the toll elasticity of expressway demand (= – demand change rate/toll change rate), it was confirmed that the average value (0-0.5) was about the same as in previous studies.
Year 2016
Doctoral Thesis
This dissertation concentrates on the problem of inferring origin-destination (OD) travel demand from multiple sources of data. The problem of OD travel demand estimation has been studied extensively in the past several decades, but new issues are still emerging when old issues are not yet fully explored. The gap between state-of-the-art and state-of-the-practice is still evident. This dissertation attempts to mitigate the gap and go beyond previous studies in using new data, building macroscopic dynamic network loading for complex multi-reservoir urban transportation network and developing novel method that incorporates perceived and observed data for estimating path flow. Chapter 3 addresses on the estimating static OD demand. The static OD ma- trices are usually derived from large scale travel survey in practice, whereas ex- isting studies consider multiple data sources for modeling such as traffic counts, probe vehicle and mobile phone data. bring a novel dataset into the forecast model framework. The Congestion Statistics data records the change of the number of dwelling people with different purposes in each mesh at each time horizons. We adopt this dataset for the following reasons: low cost, easy to collect, and privacy-free. This Chapter estimates OD demand in the forecasting framework using an updating approach. Two sequential sub-models based on the maximum entropy principle are employed to calculates trip flows of each OD pair. The first sub-model updates trip production and attraction by a non- linear optimization problem subjected to inflow and outflow, population change and the capacity of each zone. The optima correspond to the most possible trip attractions and productions in each zone. Results of submodel 1 form new constraints for updating trip matrix using a reference generated from historical data. This matrix fitting problem is dealt with by the second submodel.The proposed approach calculates trip flows of each OD pair using two sequential sub-models. Performance of the proposed methodology is validated through a numerical example and confirmed by case study using the data of Tokyo. However, the aggregate mobile phone data is not sufficient for dynamic OD demand estimation (DODE) problem. To track the time-of-day change in travel demand requires finer dataset, i.e., traffic counts. As the inverse problem of dynamic traffic assignment (DTA), the DODE estimates OD matrices by iter- atively solving the OD estimation problem and DTA problem. DTA requires a dynamic network loading (DNL) model to map path flow to path cost and an as- signment model to update path flow based experienced path cost. The classical methods for DODE problem are subject to: 1) the DNL model demands high computational ability, and 2) incorporation of multiple sources of data hasn’t yet been fully explored to improve the estimates of travel demand. Hence, Chapter 4 builds a dynamic network loading model upon the macroscopic characteristics of traffic flow depicted by Macroscopic Fundamental Diagram (MFD). The dy- namic network loading model for multi-reservoir system (MRDNL) is specified in terms of a system of partial differential equations following the conservation law, while the flows at the boundaries between reservoirs are determined by balancing the supply and demand between upstream and downstream reservoirs. Spatial discretization method and numerical scheme are also developed for vehicles’ be- havior guided by this model. The numerical method is based on the Godunov scheme to track the movement of vehicles in the network while maintaining the relevant priority rules. In comparison with previous studies, the proposed nu- merical scheme is computationally efficient, considers non-uniform cell sizes in different internal paths of a reservoir, and conserves the flow through a holding and balancing rule. A comparison with results predicted by Cell Transmission Model (CTM) shows that the new model correctly represents the traffic dynam- ics in reservoirs. Nevertheless, to divide a urban network into reservoirs is a prerequisite for enforcing the MR-DNL model. To identifying reservoirs in large network more efficiently without using the demand data, Chapter 5 presents a community detection method that yields neighborhoods in which the links are closely related and share similar traffic characteristics. The topology of network and similarity of connecting links are considered to maximize the modularity of the network. I have tested proposed method on an open data of Berlin us- ing agent-based traffic simulator. Results show that this method can identify neighborhoods in an effective and efficient way. Chapter 6 emphasizes on developing a methodology framework for estimating dynamic OD demand using traffic counts with incorporation of observed path cost. This chapter presents the primal model and a relaxed form for estimating dynamic path flow, from which the OD demand can be easily generated. This dynamic path flow estimator (DPFE) is carried over to a variational inequalities (VI) formulation accounting for the dynamic user equilibrium (DUE) principle. Implementation issues and future works are discussed in Chapter 7.
Master’s Theses
The railway share accounts for nearly 50 percentage of the transportation in Tokyo metropolitan area, which is much more higher than the other metropolises in the world. Therefore it is meaningful to research for the Tokyo rail passengers behavior. Most of the activity-based research were for work purpose, but the discretionary activities destination choice are more and more coming into notice recently. This thesis studies modeling the two discretionary activities purpose: shopping and eat out side or social. Constraint choice set by using ellipse method were created based on the GIS information of home and work places for each individual, and then the destination choice models were estimated. The small-sized zone attractiveness and combined with social characteristics estimation results are obtained, especially the destination preference for female and parents with small kids .
In this study, we examined an area-wide evaluation method for travel time reliability. First, according to the Edie’s general definition of traffic conditions within an area, we proposed an evaluation index for travel time reliability at the area level. In addition, this method is a method with low calculation and computational costs because it handles wide-area and long-term data, which is necessary for area-wide travel time reliability evaluation. By applying the proposed evaluation index to actual data, a case study was conducted for six administrative districts in the Kanto area, and it was suggested that there was no special relationship between the road maintenance status of the area and time reliability. In addition, we investigated the inflow control problem, which is considered to contribute to the improvement of travel time reliability. Specifically, by explicitly accounting for the uncertainty of the Macroscopic Fundamental Diagram in the model, a control method was developed that makes traffic conditions more stable after control. The usefulness of the proposed control method was confirmed through numerical simulations.
In urban areas, where are the core of economic development, besides the necessity of an efficient and sustainable mobility, the construction of a multimodal system is essential too. As the introduction of bus lanes is one of the useful measure, various cities are considering the introduction of bus lanes. However, when introducing bus lanes, it is necessary to evaluate their performance according to the location and amount of lanes. This study proposes a method to determine the location and amount of lanes and evaluates the network when the lanes are installed using a Macroscopic Fundamental Diagram (MFD). The MFD enables us to evaluate the road network from an areal and dynamic point of view.
Bachelor Theses
In order to quantitatively analyze and evaluate the socioeconomic impacts of railroad projects, it is essential to construct a passenger demand forecasting system that can predict the transportation behavior of railway passengers in the entire Tokyo Metropolitan Area. Especially, rail route choice model and transit assignment are the core modules of the forecasting system. However, it is still not sufficient in that a little attention is given to in-vehicle congestions and route-overlapping, both of which would have significant effects on forecasting outputs. A further refined model system was applied in the Report No. 198 of the Council for Transport Policy formulated in 2016. In this study, we aim at elaborating rail route choice model by overcoming above-mentioned problems. Specifically, we update the parameters of the C-logit route choice model, which is more computationally efficient while allowing for route overlap, with a particular focus on congestion inefficiency.
The National Main Line Passenger Net Flow Survey, which has been conducted to monitor inter-regional passenger flow, is able to capture qualitative characteristics of travelers (e.g., the purpose of travel), but it could not capture seasonal variations because it is conducted only once every five years on a specific weekday in autumn. On the other hand, the generalization of aggregated cell phone location data is making it possible to understand travek trajectory in 24 hours a day and 365 days a year, but qualitative information such as the purpose of travel cannot be obtained. In this study, we developed a method for estimating inter-regional passenger flow by travel purpose over multiple time points by merging both types of data. The estimated results were compared with the annual travel purpose composition ratios obtained from another survey (Travel and Tourism Consumption Survey), and it was confirmed that the results were generally consistent.
Year 2015
Doctoral Thesis
Traffic congestion is a widespread social problem and needs to be alleviated by sophisticated management and investment. The technological advances in monitoring traffic conditions allow the stochastic features of travel time to be better captured, which leads to many new schemes on managing the risk of travel time and thus potentially large benefits to users of transport system. The guideline of cost-benefit analysis worldwide needs to be modified into one that accounts for the benefits of emerging reliability-improving schemes. This dissertation is dedicated to the theoretical framework in including travel time variability (unreliability) into cost-benefit analysis, with a particular focus on the monetary value attached to the improvement of travel time reliability. This thesis can be divided into two parts: (1) understanding traveler’s decision when facing variable travel time and (2) modeling transport system with variable supply. The first part, including Chapter 3, is particularly concerned with estimation of the cost of travel time variability given traveler’s utility-maximizing behavior. It analyzes how systematic perception errors in travel time distribution might bias the estimates and undermine the theoretical equivalence between the structural model and reduced-form model. Empirical estimation on these biases is carried out using stated preference data. The second part, including Chapter 4 and Chapter 5, is concerned with the system (social) cost when travelers are constantly searching for lower travel cost while the transport system are constantly facing random shocks. Taking travel time variability as given, Chapter 4 uses a stylized departure-time equilibrium approach to study how system cost of a traffic bottleneck varies with travel time variability when congestion profile depends on traveler’s collective behavior. It discusses how the conventional definition of value of travel time variability can be modified and fitted in the existing framework of cost-benefit analysis for transport investment to capture the effects of endogenized congestion. On contrary, Chapter 5 challenges the assumption of stable equilibrium by showing that the system might not have a stable equilibrium in some case and travel time variability is also a phenomena of traveler’s day-to-day behavior adjustment. It uses simulation to investigate how much travelers’ day-to-day departure time adjustment contributes to the travel time variability and the time-average travel cost in a long run. In summary, the two parallel parts deal with the valuation of travel time variability from different angles, contributing new insights on using reliability as an indicator for transport user’s benefit.
Master’s Theses
The four-steps estimation method, which has been used in practice for urban railway demand forecasting in the metropolitan area, has limitations as a demand forecasting method in urban areas where lifestyles have diversified. In this study, in order to understand the lifestyle behavior of railroad users, we construct an ABM that can describe travel behavior as a part of lifestyle behavior. Focusing on the activities themselves, i.e., what railroad users do where and how they get to the location of their activities, we represent an individual’s daily life behavior by activity pattern, time of day, destination, route, and access mode. The model was estimated based on a person-trip survey, and it was confirmed that the model has a certain degree of reproducibility to the current situation.
In the Tokyo metropolitan area, while measures such as increasing the number of trains in the morning congestion period and direct-through trains have improved convenience, chronic train delays have been occurring, resulting in a decline in punctuality. Although some simulation studies of train delays have been conducted, there are no studies that investigate the stochastic characteristics of delay phenomena. The objective of this study is to construct a probabilistic model of train delays in urban railroads that takes into account the spatio-temporal correlation between trains in front of and behind stations. The train operation data of the Tokyo Metro Tozai Line over a long period (about two years) is adopted. This made it possible to evaluate the likelihood of delays occurring for each event, such as running between stations and stopping at stations..
Bachelor Theses
Logistics is one of the essential elements in people’s lives in modern society. In the Tokyo metropolitan area, the development of transportation infrastructure such as the three ring roads has been progressing recently, and the location of logistics facilities has also been changing. In this study, we modeled the location and quantity of logistics facilities in Kanagawa Prefecture, Japan, using the results of the Tokyo Metropolitan Area Freight Flow Survey. Although there have been previous studies on location selection models, this study aimed to construct a discrete-continuous choice model that predicts the choice behavior of location and location quantity (site area of facilities) for each cubic mesh (approximately 1 km square), and to construct a more valid model by considering spatial correlation. The model stimation results revealed that the convenience of surrounding roads and zoning had a significant impact on location behavior.
The railway network in Tokyo consists of multiple operators. When going to a certain destination, there are routes that connect to multiple operators, but fares are added for each operator, giving users the impression that they are paying a premium for the service. This may cause a “selection distortion” in which users choose routes that are not optimal in terms of time required and number of transfers because of their low fares. In this study, we clarified the influence of the fare system of each operator on users’ choice behavior, and constructed a route selection model for railway users that can comprehensively consider the factors on the users’ choices. Then, we simulated the effect of introducing common fares as a way to eliminate selection distortion.
Year 2014
Master’s Theses
This study analyzes citizens’ travel choice behavior in a medium-sized Southeast Asian city to observe their intention to use new public transport. We selected Malang in Indonesia as a case study. A travel behavior and intention survey including stated preference questions was conducted with university students. The results of the latent-class model of commute mode choices show that respondents could be divided into “cost and delay time” and “travel and access time” oriented classes. Respondents who were likely to convert to new public transport modes were male, had a higher income, and were interested in new public transport. The estimation results of the scheduling choices model confirm the significant difference in the sensitivity to recreation time between recreational activities.
The travel time reliability is a major concern for drivers, especially for users who do not like the risk of being late, and the uncertainty of arrival time reduces satisfaction with road use. One way to mitigate this problem is to use the hyperpath-based risk averse route guidance, which recommends the shortest possible route under travel time uncertainty. In this study, we developed a route guidance system that can be adapted to real-world road networks to avoid the risk of being late. Through running some experiments, we verified the effectiveness of this route guidance system on travel time reliability. The results suggest that the system is effective in suppressing the variation of travel time, especially the effect of significantly reducing large delay time, compared to the route guidance based on ordinary shortest route search.
In this study, considering the near-future road traffic in which the number of drivers following tardiness risk-avoiding route selection based on the hyperpath (HP) concept will gradually increase, we evaluate the impact of the spread of HP on network flow. Based on the traffic flow simulation, the basic characteristics of how the performance of the entire network (e.g., average travel time and travel time variation) changes when the real road network in the Tokyo metropolitan area (e.g., traffic volume, network size, HP car navigation penetration rate, etc.) is changed are clarified. Next, the impact of the introduction of HP on the network flow is estimated for a real road network in the Tokyo metropolitan area.
Bachelor Thesis
Clarifying which factors cause traffic volume and travel time to fluctuate over time is useful not only from the perspective of efficient roadway operation, but also for project evaluation in the consideration of travel time reliability. This study comprehensively estimates the factors of traffic volume fluctuation (trend fluctuation, seasonal and day-of-week fluctuation, policy fluctuation, etc.) using long-term time-series data of monthly and daily traffic volumes on expressways. By applying a structural time-series model, one of the special systems of the general state-space model, to the traffic volume data of Japanese intra- and inter-city expressways (Hanshin Expressway, Metropolitan Expressway, and NEXCO), we extracted each variable component. In particular, we estimated the intervention effect of expressway toll policies (e.g., 1,000 yen discount for holidays, distance charge, etc.).
Year 2013
Master’s Theses
Electricity liberalization has the advantage of economic efficiency, such as making it easier for technological innovation to occur because it intensifies competition. However, in countries such as the United States, which have undergone full liberalization, it has been pointed out that the liberalization has weakened the network. In this study, we evaluated and compared the vulnerability of two electricity supply networks, one with traditional partial vertical integration and the other left to the market after liberalization, by modeling them using a network equilibrium model. The results showed that the latter network, which assumes post-liberalization conditions, is more efficient under normal conditions due to the optimal allocation of resources. However, the Importance Value, which indicates dependence on a single facility, was found to be increased. It quantitatively suggested that the network has the potential to become more vulnerable after electricity liberalization.
In recent years, the economic damage caused by natural disasters has been increased. It has been pointed out that natural disasters may have a significant impact on macroeconomic growth at the national level. In this study, we first statistically examine the impact of natural disasters on the rate of economic growth through an econometric analysis using time-series macroeconomic data at the national level. The results showed that natural disasters had no significant effect on the GDP growth rate of the country as a whole, but had a significantly negative effect in the agricultural sector and a significantly positive effect in the industrial and service sectors. Next, a stochastic dynamic general equilibrium model was constructed to structurally understand the impact of natural disasters on economic growth. The simulation results suggest that the effect of technological innovation associated with disasters differs between social welfare and production.
Given the limitations of new urban railway construction in Tokyo metropolitan area, the time-varying fare policy is expected to be the most effective measure to spread the concentrated peak demand. This paper firstly serves as an empirical study of the theoretical time-varying marginal utility model introduced by Vickrey (1973) with the data of urban rail commuters in Tokyo. Secondly, the departure-time-choice model under deterministic user equilibrium is extended by integrating with the empirically identified time-varying marginal utility model. The outputs of the equilibrium model are compared with the one with the traditional constant marginal utility model and we find that the former outputs would be more suitable for the commuting pattern with longer travel distance like the case in Tokyo. The equilibrium scheduling pattern and the first-best pricing strategy are examined, which demonstrates the time-varying marginal utility model can capture the marginal external cost more precisely for the travellers with relatively flexible arrival time.
In this study, we analyzed the simultaneous airport-access choice behavior of air passengers in the Tokyo metropolitan area, which has two or more international airports, Haneda and Narita, using the International Air Passenger Survey after the internationalization of Haneda in 2010. The analysis showed that the frequency of flight, place of residence, and annual income determine the airport-access mode choice behavior. Next, a non-aggregate analysis using a nested logit model revealed that airfare, flight frequency, and access time/flight time were the main factors in choice behavior, and that the sensitivity of access time differed depending on the flight distance zone. It was also shown that the uncertainty of access time has a negative utility. Finally, the elasticity of each transportation mode’s share due to the reduction of access time for Narita Airport bound railroads was calculated, and it was shown that the shift in demand between airports is less likely to occur than the shift in demand between modes.
Bachelor Theses
The multinomial probit model, which has been used to describe the route choice behavior of passengers in dense railway networks, cannot explicitly solve the integral calculation of the multivariate normal distribution contained in the model. Hence, the approximate calculation based on the Monte Carlo method has been applied. On the other hand, in the practice of railroad demand forecasting, the detailed passenger demand allocation is required, so there is a need to improve the calculation speed while satisfying accuracy requirements. This study applies four analytical integral approximation methods to the Probit model and clarifies the characteristics of each method through numerical analysis. We also applied the methods to passenger assignments for the metropolitan rail network, and compared the accuracy and computational efficiency of the methods with those of conventional methods. Through the above, we clarified the certain usefulness of the analytical integral approximation method.
Model analysis of the effect of platform door installation on train delays on urban railroads(菊池 恵和)
Although platform doors can prevent personal injury, their installation leads to an increase in the time trains remain in the station, which may reduce the utility of passengers. However, assuming that the platform doors start closing at the same time as the train doors and prevent boarding just before the train doors close, one hypothesis is that the installation of platform doors improves the reliability of the train schedule. This study examines whether the installation of platform doors affects the punctuality of train service on a single line based on a mathematical model. The comparison through simulation suggests that although the amount of train delay increases with the installation of doors, the disutility of user travel may not necessarily increase significantly due to the passengers’ choice of train.
Year 2012
Doctoral Theses
Congestion problems of urban railway, including the Tokyo metropolitan area in Japan is one of the transportation policy issues that need to be resolved. The purpose of this study is to develop a quantitative analysis method to describe the behavior of the passenger rail network and stations under congestion. First, in order to describe the behavior of passengers on the network, I have developed a frequency-based route allocation model that takes into account the delay due to congestion and congestion in the train line. On top of that, we have carried out the implementation of the distributed computing system to assume the fast path network application to large-scale parallel processing was introduced. Next, to describe the congestion in the station, to build a model with endogenous walking behavior selection sequential destination, we have carried out the implementation of the micro-simulation system. At that time, in order to acquire data efficiently pedestrian behavior is essential to estimate the model, we have developed a data acquisition system behaves incorporated image analysis techniques.
This research has studied the theoretical model and algorithms for hyperpath routing under travel time uncertainty. Many efforts have been made on static hyperpath generation with historical data while the real-time route guidance has not been studies. The idea of hyperpath which originates from the field of frequency-based transit assignment has provided a novel and promising way of routing by recommending a prior potentially optimal link set instead of a specific route, which implies an adaptive routing strategy. Consequently this research focuses on hyperpath-based route guidance and several related issues have been studied. First of all, based on an earlier study on using hyperpath for route guidance, the theoretical model of risk-averse routing with uncertain travel times is formulated. The proposed model reduces to the conventional shortest path model when the network is certain. Furthermore, the relation between the risk-averse routing model and hyperpath model is built with several mathematical transitions. The performances of these algorithms including the existing ones are tested with networks of different topologies, sizes and delay levels. One of algorithm variants, namely SFdi algorithm, is recommended for solving hyperpath generation on real road networks. After the algorithm is conceived of, on purpose of continuing other related studies, GIS software tools are developed with the support of open sources. Two tools, namely GeoRotuing.Net and PyGeoRouting based on different framework are introduced after an introduction of technical issues about route planning with the help of GIS tools. The hyperpath model proposed in based on risk aversion results in a risk-averse potentially optimal link set. The addition of risk-aversion causes the fact that conventional shortest paths may get excepted from the hyperpath. This leads to a different consideration of the hyperpath without any risk-averse assumption, namely potentially optimal hyperpath (PO). The PO hyperpath may incur risk since risk-aversion is not considered in PO hyperpath generation and regret minimization is considered to avoid risky routing. Several prior routes are evaluated by Monte Carlo simulation and one of proposed regret-based routing turns out to be better or at least no worse than others. As an alternative method of adaptive routing, hyperpath is proposed as a prior risk-averse potentially optimal link set and the guidance should be based on real-time traffic data. Considering the fact that such real-time may not always available, a complementary method which recommends several a prior routes is also proposed. The route recommendation is based on reliability index and dissimilarity index. When real-time traffic data are unavailable, travelers can still rely on these a prior routes.
Master’s Theses
The vulnerability of national land structure, such as unipolar concentration type to major disasters, has been pointed out. In this study, we regard the state in which the impact of a disaster spreads widely in space and time as a state of high disaster vulnerability. A basic economic model analysis was conducted to determine which kind of national land structure with a population distribution is desirable. More specifically, we constructed a stochastic multi-regional dynamic macroeconomic model that considers investment adjustment costs and the impact of social capital, and constructed a framework for evaluating national land structure based on disaster vulnerability indices. Numerical simulation results suggested that a more desirable national land structure may differ from the viewpoint of maximizing social welfare and the viewpoint of minimizing the disaster vulnerability of the nation as a whole.
Though the development of real-time traffic information and vehicle navigation has contributed to the increase in drivers’ satisfaction, the market diffusion of these technologies may not lead to the reduction of traffic congestion mainly due to the concentration of traffic into particular paths or links in the traffic networks. Therefore, this study analyzes the impact of risk-averse route guidance based on the Hyperpath concept on traffic flow by performing dynamic route allocation using a simulation method. The hyperpath-based route recommendation would have the potential of reducing the congestion of the entire network because it recommends a potential optimal set of paths instead of the shortest (single) path and lead to the dispersion of traffic in an appropriate way. This study analyses the market diffusion effects of hyperpath-based route recommendation on the whole network traffic by employing agent-based traffic simulation mid dynamic traffic assignment. Some comparison studies reveal that indeed the hyperpath-based route recommendation would contribute to the mitigation of traffic congestion in some aspects.
This paper proposes a nonparametric estimator with monotonic constraints, and applies it to binary choice model with parameters lying on willingness-to-pay space. With simulated data we validate that the constrained estimator has better property when estimating c.d.f.. Subsequently a case study using stated preference data is carried out for obtaining the VTT distribution for Japanese car users. We find that 1) a relatively big gap between constrained and unconstrained VTT estimates exists 2) the unconditional VTT is likely to be Johnson’s S B distributed and 3) the mean VTT in Japan is about 9.51 JPY/min.
The necessity for high-density sensor installations and redundancy of sensor information in traffic state estimation is of concern to researchers and practitioners. The influence of different sensor locations on the accuracy of traffic state estimation using a velocity-based cell transmission model and state estimation with an Ensemble Kalman Filter was studied and tested on a segment of the Tokyo Metropolitan Highway during rush hours. It showed the estimated velocity changes significantly when the interval is extended from 200 m to about 400 m, but is acceptable at about 300 m. Sensor locations are critical when reducing sensor numbers.
Bachelor Theses
This paper develops a dynamic discrete-continuous model for analyzing households’ multiple vehicle ownership (lightsized vehicle, standard sized vehicle or their combinations) and their usage (vehicle distance travelled per year). The model is calibrated by using Bayesian estimation to explore the determinants of households’ mobility decision with a nationwide large-scale panel survey which has been continuously conducted in Japan for years. We find that income and number of female drivers would affect the changes in vehicle ownership pattern (i.e. positive impacts on the propensity to own standard-sized vehicles more than light-sized ones). While state-dependencies among ownership and among usage have been confirmed, a clear correlation structure has not been confirmed between ownership and usage.
This study conducted an empirical analysis of the relationship between urban structure and individual travel behavior, with a particular focus on the influence of urban structure on individual public transportation use. Specifically, using individual data from the 2010 National Urban Transport Characteristics Survey, we aimed to understand how urban characteristics and individual attributes affect the propensity to use public transportation and the proportion of public transportation and car uses. Logistic regression models confirmed that the degree of urbanization, the degree of urbanization, and the convenience of public transportation had a significant effect on car use or public transportation use.
Year 2011
Bachelor Theses
In this study, we analyzed the prediction of travel time reliability indices from two perspectives: improvement of existing models and construction of new models. Using a large amount of ETC data, we were able to identify most of the factors that affect the travel time reliability. Next, the possibility of integrating travel time reliability indices across adjacent links was examined with respect to the covariance value of travel time. Although it was not possible to construct a predictive model that was significant enough to estimate the travel time covariance, it was found to be consistent with the magnitude relationship of continuous upstream and downstream traffic volumes.
In this study, we conducted a model analysis of the impact of the request to railroad operators to save electricity due to rolling blackouts on the convenience of passengers in the Tokyo metropolitan area railroad network. Specifically, based on Spiess and Florian’s (1989) least-cost Hyperpath approach, we visualized how generalized costs changed by expressing users’ route selection behavior. The generalized cost was calculated taking into account the use of detour routes, which are not usually used, by focusing on changes in hyperpath before and after the planned power outage..
Year 2010
Master’s Theses
The decline in regional vitality is now a serious problem throughout Japan. Specifically, the hollowing out of city centers and the decline of commercial functions are becoming more serious as motorization progresses and consumer lifestyles change. In particular, many depopulated areas in the countryside are facing an exodus of the working population, which threatens their very survival. Various market-based initiatives have been promoted to revitalize regions. However, there have been insufficient empirical studies on the adverse effects of such efforts. Based on Hirschman’s theory, this study aims to formulate a hypothesis regarding the relationship between “disengagement” and “voice” in local communities, and to empirically examine the effect of the increase in the means of disengagement on the means of voice. To empirically test the hypothesis, we conducted a questionnaire survey of shopkeepers belonging to the Meguro Ward Federation of Shopping Centers. The results of the hypothesis test indicated that people who are not in the shopping district tend not to speak out, that people who are not in their own shopping district tend to make short-term and private comments, and that people who are highly loyal to the shopping district tend not to leave the shopping district and to speak out for the shopping district. Those who are highly loyal to the shopping arcade tend not to leave it and to speak up for it.
The automobile has played an indispensable role in industry and daily life, but the circumstances surrounding the automobile have changed dramatically due to global environmental issues, fluctuating gasoline prices, and the increasing convenience of public transportation. In particular, CO2 emissions from automobiles account for about 90% of the total emissions from the transportation sector, making the reduction of CO2 emissions from automobiles an urgent issue. In response to this situation, automobile manufacturers are working on technological innovations to improve fuel efficiency, while the government has been promoting environmentally friendly vehicles through policies such as tax breaks for eco-cars. Although both technological and policy measures appear to be effective in reducing CO2 emissions from automobiles at first glance, there has been some debate in recent years that these measures may in fact encourage the use of automobiles, which in turn may lead to increased CO2 emissions. In this study, we focus on policies to improve fuel efficiency and promote the spread of environmentally friendly vehicles, and analyze the effects of these policies on regional automobile traffic volume using long-term time-series panel data. In addition to the aforementioned factors, the effects of gasoline price fluctuations, road congestion, and sharing with railroads were also examined.
Truck transportation accounts for the majority of freight transport in Japan, and it is also responsible for a large proportion of carbon dioxide emissions. In addition, the diversification of economic activities in recent years has led to expectations for improved logistics services. In particular, the need for time-specified delivery has been established as a minimum required service. Therefore, logistics service providers must accurately determine the time and select delivery routes. However, travel times are continuously changing due to various factors. Therefore, logistics service providers must take into account the uncertainty of travel times when selecting delivery routes. This study uses truck probe data to understand the relationship between travel time variation and actual route selection behavior. After that, by applying the truck probe data to an integrated model, we estimated the travel time reliability value and examined the feasibility of introducing the estimated value into a cost-benefit analysis.
Direct-through service between multiple urban railroads has played a major role in eliminating passenger transfers and easing terminal congestion. However, delays have become common due to on-board congestion and high frequency operation. Moreover, the direct-through service operation has the detrimental effect of spreading delays over a wide area. The purpose of this study is to construct a mathematical model to evaluate the difference in propagation of train delays and the accompanying changes in passenger behavior on a hypothetical railroad line. Theoretical considerations were also made regarding the optimal frequency of direct train service and the optimal operating section of the line by varying the number of passengers and the length of the line.
Bachelor Theses
Dhaka, the capital of Bangladesh, is a megacity with a population of 10.7 million, or 7.5% of the country’s total population, in its metropolitan area (Dhaka Metropolitan Area: DMA), and is known for its extremely high population density. Currently, the urban transportation in the DMA is heavily dependent on road transportation, mainly bus transportation, which causes serious traffic congestion, traffic chaos, air pollution, and health problems. Aiming to formulate a basic urban development plan for the Dhaka metropolitan area by 2025, the Dhaka urban transportation network development project preparatory study (DHUTS) is currently underway, which includes a person trip survey, traffic volume survey, and preference survey for the introduction of track-based transportation systems. In this study, a disaggregate transportation mode choice model by trip distance and income group was constructed and estimated using the DHUTS transportation survey conducted in 2009 to analyze transportation mode choice behavior in the DMA.
The purpose of this study is to construct a pedestrian behavior model considering the pedestrian flow. Although there have been many studies on pedestrian behavior, several issues remain. First, there is often a lack of support from actual data. In this study, we obtain actual pedestrian flow data in a station and identify model parameters based on the data. Second, it is difficult to take into account pedestrians’ destination choices. In this study, a new behavioral model called the Plan-Action Model is used to simultaneously model dynamic destination and route selection by pedestrians. In the empirical analysis, we constructed a model that integrates the pedestrian’s choice of a ticket gate with his/her route selection, using the space near station ticket gates, which is congested during commuting hours as the target. Finally, we developed a simple pedestrian behavior simulator based on the model.
This study examines whether the introduction of ETC had an effect on toll elasticity. The basic policy of the analysis is a macro-economic analysis using multiple regression equations with traffic volume as the explained variable. The results of the empirical analysis indicate that the number of vehicles using the ETC system has increased due to the ETC discount, while short-distance trips may have increased in response to the discount system that is applied within 100 km, such as early morning and evening discounts. Moreover, the introduction of the ETC system has reduced the elasticity of tolls, in other words, the effect of cashless travel, and that the introduction of the ETC system has reduced the elasticity of tolls on major routes.
Year 2009
Doctoral Thesis
Information and Communication Technology (ICT) has the potential to induce or reduce physical travel. And recently, the impact of social dimension on activity-travel has just gained considerable attention in the realm of transportation planning. This study explores the potential effects of both information and communication technology and social dimension on travel behavior in the following aspects. (1) The effects of mobile phone and telecommuting as ICT are analyzed to investigate Londoner’s travel behavior by focusing mainly on trip frequency, number of tours and tour complexity. The results of our descriptive and multivariate regression analysis imply that mobile phone possession significantly and positively affects total trips made though not necessarily tour complexity. The study provides good evidence that mobile phone possession is clearly associated to total tours made. Though telecommuting does decrease work trips, other trips like shopping or leisure trips are likely to increase. (2) The effects of social dimension such as social interaction, social activities, social network and time planning on travel behavior are examined through the case study in Metro Manila, Philippines. Initially, the effects of socialization on travel are investigated with focus on university students’ activity-travel behavior as influenced by the level and form of their socializing practices. It is hypothesized that socialization would greatly affect the number of side-trips students took while returning home after class. The results may imply that socialization provides sound motivation for trip generation and might be prospect for consideration in the future development of transportation planning processes especially in the developing countries. (3) In addition, the effects of social dimension on travel are examined in the context of university workers in Metro Manila. Social dimension includes social interaction, social activities and social network. The estimation results indicate that there exists a positive and significant effect of social interaction on social network and social activities. Social interaction also has an indirect positive and significant effect to social activities via social network. These findings imply that social factors play an essential role in the study of travel behavior in developing countries. Similarly, the effects of ICT use on time planning, social activity participation, social network on travel behavior are further investigated.
Master’s Theses
In recent years, in the evaluation of road projects, in addition to the typical three benefits of reduced travel time, reduced traffic accidents, and reduced transportation costs, consideration has been given to the inconvenience benefit of increased uncertainty due to greater fluctuations in travel times due to traffic congestion and other factors. The concept of dealing with this fluctuating travel time is travel time reliability. In this study, aiming to contribute to the construction of an economic benefit measurement method for improving travel time reliability in Japan, an attempt was made to estimate travel time reliability value using a new model that integrates a driver’s scheduling model and a mean-variance model. A behavioral model was estimated using the choice data obtained from the Stated Preference Survey, and it was confirmed that a reliability ratio comparable to that of previous studies was obtained. In addition, we also considered the tendency of the time reliability value seen by individual attributes.
From the viewpoint of social dilemma, physical measures such as removal of bicycles and increased fines have been mainly implemented, while psychological measures have not been sufficiently examined. Based on this background, this study first verified the effectiveness of communication-based measures to reduce abandoned bicycle parking in railroad stations and university campuses, where several findings have been accumulated to date. Next, we focused on the awareness of attachment to bicycles and examined the possibility of reducing the number of abandoned bicycles by means of measures to activate this awareness. Finally, the secondary effect of removing abandoned bicycles was examined from the viewpoint of “alienation from the community”.
The purpose of this study is to evaluate passenger flow lines in airport terminals comprehensively through the systematic clarification of the multifaceted functions of terminals and the various ways of thinking of users. For this purpose, a system of evaluation items and an evaluation index were established for passenger flow lines in airport terminals. Furthermore, we conducted surveys of passenger flow lines at airports in various countries and regions to obtain evaluation indices, and attempted to objectively identify the characteristics of each airport terminal. We also studied a methodology for systematically clarifying airport user’s attitudes.
Bachelor Theses
This study introduces a route choice model of the public transportation proposed by Spiess and Florian and Nguyen and Pallottino, and examines its applicability to the metropolitan rail network. Specifically, we attempted to apply a route choice model based on the Hyperpath concept, which explicitly takes into account waiting times at platforms under the assumption of the common lines problem. The usefulness of the model was verified on a small-scale real network.
Pedestrian simulation based on discrete choice pedestrian behavior models has the potential to contribute to detailed facility design of walking spaces. However, to estimate the unknown parameters of the model, it is necessary to acquire a large amount of pedestrian behavior data with high accuracy, and the development of an efficient data collection method is desired. In this study, we conducted a basic study on the effectiveness of an automatic pedestrian behavior data extraction method using image analysis technology. Specifically, we compared a data collection method based on background differences developed by the authors with a newly proposed method using particle filters. We estimated behavioral models using data sets obtained by both methods and compared the accuracy and stability of the two methods. The results showed that the newly proposed method is more accurate and the data can be acquired in real time.
Year 2008
Master’s Thesis
This study develops a method for estimating the Valuation of Travel Time Variability (VTTV), which is necessary for economic evaluation of the improvement of timeliness in car traffic. First, a microeconomic model describing drivers’ departure time choice behavior under the uncertainty is developed. Next, we used travel time data obtained from an expressway ETC system to verify whether the assumptions necessary for the actual application of the theoretical model are satisfied, and calculated the ratio of VTTV to the value of time saved. Finally, we calculated the change in total cost to the driver using the proposed method and estimated the economic benefits of improving the timeliness of travel before and after the implementation of the measure.
Bachelor Theses
In recent years, one of the major changes in the structure of the automobile market is that the number of vehicles owned and the number of license holders have increased since 2003, while the number of vehicle kilometers driven has decreased. The purpose of this study is to analyze the structure of multiple car ownership and use, taking into account household and regional characteristics, and to construct a model that simultaneously determines car ownership and use using a discrete-continuous model. The most important feature of this study is that household characteristics, regional characteristics, and multiple ownership are taken into account using such large-scale data. Based on the data analysis and model construction described above, this study finally examines the effects of gasoline prices and changes in road maintenance conditions on automobile ownership and usage through sensitivity analysis.
In order to construct a pedestrian behavior model that contributes to the development of facility design proposals for congested walking spaces such as train stations, we applied a discrete choice model that can flexibly consider the effects of various spatial conditions based on speed and direction. In addition, to perform pedestrian simulation according to the discrete choice model, it is necessary to obtain spatiotemporal coordinate information on the pedestrian’s movement trajectory and relative positional relationship with other pedestrians. We also built an algorithm to automatically detect pedestrians with high accuracy through analysis.
Year 2007
Bachelor Theses
In metropolitan areas, there is an excessive dependence on automobiles for short-distance travel.
Moreover, a mobility gap is thought to exist between the distance that can be traveled on foot and the distance that can be traveled by public transportation. In this research, to fill the mobility gap, we focus on a new small portable electric transportation means ‘PMV (Personal Mobile Vehicle)’. We conducted an experimental study on “understanding the trip distance range that will be covered”, “understanding the psychological factors that determine awareness of use”, and “promoting use of the PMV and improving its social acceptability”.
In the automobile sector, the most important index for studying global warming countermeasures and energy saving measures is the fuel consumption during actual driving (actual fuel consumption). A macro estimation model that evaluates the effects of geographical and social characteristics of automobile usage areas on actual fuel consumption is useful for studying measures against global warming on a nationwide level, such as improving the average speed, but there are only a few examples of such studies. In this study, we developed a macro estimation model of actual fuel consumption using data on actual fuel consumption of automobiles obtained from a nationwide large-scale survey conducted in Japan in recent years.